
The hemorrhage may be secondary to a head trauma. The subarachnoid hemorrhage follows the gyri sulci pattern and spreads out over the left convexity. The blood is located between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater.įigure 13. Detailed illustration of a subarachnoid hemorrhage. The subarachnoid spaces include the basal cisterns (= space around the brain stem), the Sylvian fissure, the cerebral sulci, the intraventricular space and the interhemispheric fissure (fig.13).įigure 12. In a subarachnoid hemorrhage, the blood is located in the subarachnoid spaces (fig. Overview of a number of important subarachnoid cisterns in the sagittal plane. cisterna magna (cerebellomedularis) caudal of the cerebellum and dorsal of the medulla oblongata.įigure 8.prepontine cisterns (transversal moon shape).suprasellar cisterns (transversal pentagon/5-sided shape).quadrigeminal cistern (transversal W shape).Sylvian fissure space between the temporal and frontal lobes.These spaces are filled with CSF and in some places also surround arteries/veins/cranial nerves.Ī few important subarachnoid cisterns include (fig. The subarachnoid space is enlarged in certain places the subarachnoid cisterns. Resorption of CSF through the arachnoid granulation in the venous sinus. Circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid in the coronal plane (a) and sagittal plane (b).įigure 7. The CSF acts as a transport medium of nutrients and waste and as a cushion for the brain and spinal cord.įigure 6. Resorption takes place in the venous sinus (through the arachnoid granulation, fig 7). The CSF then flows through the foramina to the subarachnoid space over the convexity of the brain and around the spinal cord (fig. The CSF circulates from the ventricles (through the 3rd ventricle & the aqueduct) to the 4th ventricle. 5).Ĭerebrospinal fluid, often abbreviated as CSF, is produced in the choroid plexus, located in the ventricles.
The inner layer of the dura mater has deep folds (= dural folds) into the skull the cerebral falx and cerebellar tentorium (fig. The outer layer of the dura mater is attached to the skull roof.

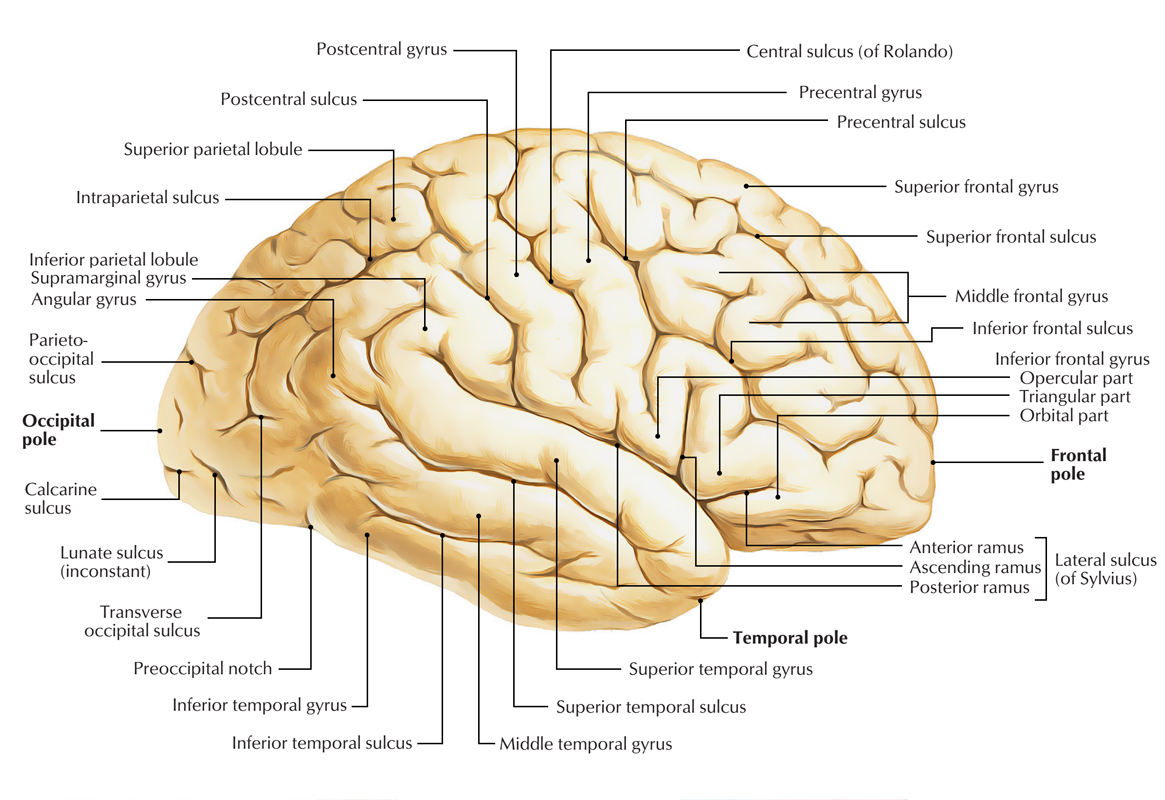
In this space are blood vessels and the cerebrospinal fluid.Ī venous hemorrhage may cause an artificial subdural space between the arachnoid mater and dura mater (see subdural hematoma in Pathology section). The physiologic subarachnoid space consists of a fine web of collagen/elastic fibers and is located between the pia mater and arachnoid mater. The brain is covered from inside out by the pia mater, the arachnoid mater, the dura mater and the skull roof (fig. The Sylvian fissure (= lateral fissure) separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe. The frontal and parietal lobes are separated by a deep groove, the central sulcus (= Rolando’s fissure). The two hemispheres are subdivided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe and the occipital lobe (fig. Normal brain anatomy in the transversal plane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
